这是一份 Imperial帝国理工大学 PHYS96039作业代写的成功案例
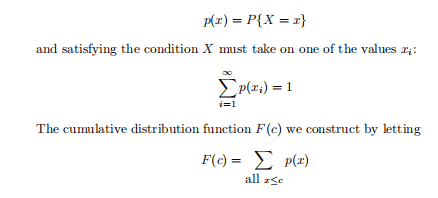
When $X$ is a discrete random variable,
$$
\begin{aligned}
E[a X+b] &=\sum_{i}\left(a x_{i}+b\right) p\left(x_{i}\right) \
&=a \sum_{i} x_{i} p\left(x_{i}\right)+b \sum_{i} p\left(x_{i}\right) \
&=a E[X]+b
\end{aligned}
$$
\begin{aligned}
When $X$ is a continuous random variable,
$$
\begin{aligned}
E[a X+b] &=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}(a x+b) f(x) d x \
&=a \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x f(x) d x+b \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x) d x \
&=a E[X]+b
\end{aligned}
$$

PHYS96039 COURSE NOTES :
$$
\sum_{j=1}^{l} a_{j}=N
$$
The total energy of the ensemble is assumed to be fixed as well. This yields our second constraint:
$$
\sum_{j=1}^{l} a_{j} e_{j}=E
$$
Let the vector $\mathbf{a}=\left(a_{1}, a_{2}, a_{3}, \cdots a_{l}\right)$ describe the occupation numbers of a system. Define $\Omega(\mathbf{a})$ to be the number of ways that the virtual systems can occupy the $l$ states. Then
$$
\Omega(\mathbf{a})=\frac{N !}{\prod_{j=1}^{l} a_{j} !}
$$