这是一份manchester曼切斯特大学 MATH32032作业代写的成功案例
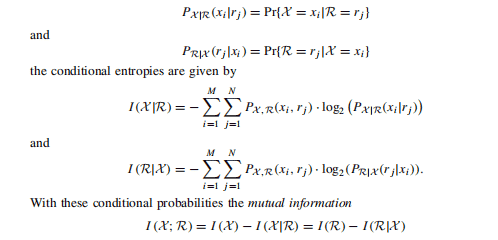
A $q$-nary block code $\mathrm{B}(n, k, d)$ with code word length $n$ can be illustrated as a subset of the so-called code space $\mathbb{F}_{q}^{n}$. Such a code space is a graphical illustration of all possible $q$-nary words or vectors. 4 The total number of vectors of length $n$ with weight $w$ and $q$-nary components is given by
$$
\left(\begin{array}{l}
n \
w
\end{array}\right)(q-1)^{w}=\frac{n !}{w !(n-w) !}(q-1)^{w}
$$
with the binomial coefficients
$$
\left(\begin{array}{l}
n \
w
\end{array}\right)=\frac{n !}{w !(n-w) !}
$$
The total number of vectors within $\mathbb{F}{q}^{n}$ is then obtained from $$ \left|\mathbb{F}{q}^{n}\right|=\sum_{w=0}^{n}\left(\begin{array}{c}
n \
w
\end{array}\right)(q-1)^{w}=q^{n} .
$$

MATH32032 COURSE NOTES :
of choosing $w$ out of $n$ positions, the probability of $w$ errors at arbitrary positions within an $n$-dimensional binary received word follows the binomial distribution
$$
\operatorname{Pr}{w \text { errors }}=\left(\begin{array}{c}
n \
w
\end{array}\right) \varepsilon^{w}(1-\varepsilon)^{n-w}
$$
with mean $n \varepsilon$. Because of the condition $\varepsilon<\frac{1}{2}$, the probability $\operatorname{Pr}{w$ errors $}$ decreases with increasing number of errors $w$, i.e. few errors are more likely than many errors.
The probability of error-free transmission is $\operatorname{Pr}{0$ errors $}=(1-\varepsilon)^{n}$, whereas the probability of a disturbed transmission with $\mathbf{r} \neq \mathbf{b}$ is given by
$$
\operatorname{Pr}{\mathbf{r} \neq \mathbf{b}}=\sum_{w=1}^{n}\left(\begin{array}{l}
n \
w
\end{array}\right) \varepsilon^{w}(1-\varepsilon)^{n-w}=1-(1-\varepsilon)^{n} .
$$