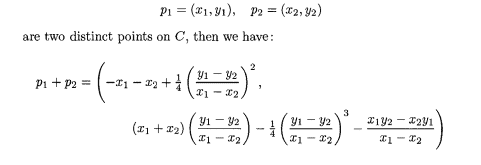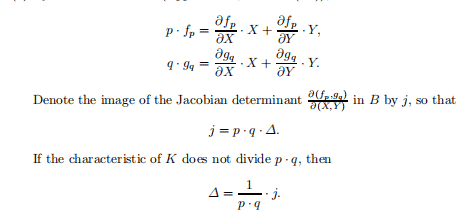
$$
\operatorname{dim}{K} \frac{\overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P}}{\mathcal{O}{F, P}}+\operatorname{dim}{K} \frac{\mathcal{O}{F, P}}{(\gamma)}=\operatorname{dim}{K} \frac{\overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P}}{(\gamma)}+\operatorname{dim}{K} \frac{\gamma \overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P}}{\gamma \mathcal{O}{F, P}} .
$$
Since $\gamma$ is not a zero divisor of $\overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P}$, the $K$-vector spaces $\overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P} / \mathcal{O}{F, P}$ and $\gamma \overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P} / \gamma \mathcal{O}_{F, P}$ are isomorphic, and so
$$
\mu_{P}(F, G)=\operatorname{dim}{K} \overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P} /(\gamma) .
$$
As in the proof of we have
$$
\overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P} /(\gamma) \cong R{1} /(\gamma) \times \cdots \times R_{h} /(\gamma)
$$
and then from E.13,
$$
\operatorname{dim}{K} \overline{\mathcal{O}}{F, P} /(\gamma)=\sum_{i=1}^{h} \operatorname{dim}{K}\left(R{i} /(\gamma)\right)=\sum_{i=1}^{h} \nu_{R_{i}}(\gamma)
$$

MATH0076 COURSE NOTES :
$$
\varepsilon: S\left[X_{1}, X_{2}\right] \rightarrow A[X, Y] \quad\left(X_{1} \mapsto X, X_{2} \mapsto Y\right)
$$
and
$$
\delta: S\left[X_{1}, X_{2}\right] \rightarrow B[X, Y] \quad\left(X_{1} \mapsto X, X_{2} \mapsto Y\right) .
$$
Here $\varepsilon(F)=f, \varepsilon(G)=g, \delta(F)=G f, \delta(G)=G g$, so that by $\varepsilon$ the induced epimorphism
$$
S\left[X_{1}, X_{2}\right] /(F, G) \rightarrow A[X, Y] /(f, g)
$$
can be identified with the canonical epimorphism $S^{e} \rightarrow A^{e}$ and
$$
S\left[X_{1}, X_{2}\right] /(F, G) \rightarrow B[X, Y] /(G f, G g)
$$
with $S^{e} \rightarrow B^{e}$.