这是一份kcl伦敦大学学院 5CCM211A作业代写的成功案
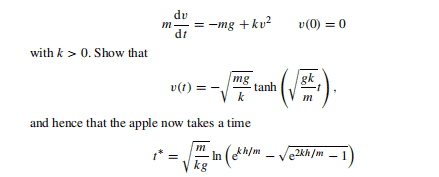
$$
\mathrm{e}^{p t}\left(\frac{\mathrm{d} x}{\mathrm{~d} t}+p x\right)=q \mathrm{e}^{p t}
$$
and using this is simply
$$
\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d} t}\left(x \mathrm{e}^{p t}\right)=q \mathrm{e}^{p t} .
$$
For the general solution we integrate both sides to give
$$
x(t) \mathrm{e}^{p t}=\frac{q}{p} \mathrm{e}^{p t}+C,
$$
so that
$$
x(t)=\frac{q}{p}+C \mathrm{e}^{-p t} .
$$
(It follows that if $p>0$ then $x(t) \rightarrow q / p$ as $t \rightarrow \infty$, independent of any initial condition.)
If we want the solution that has $x(a)=x_{a}$ then we need
$$
x_{a}=\frac{q}{p}+C \mathrm{e}^{-p a} \quad \Rightarrow \quad C=\left(x_{a}-\frac{q}{p}\right) \mathrm{e}^{p a}
$$
and so this solution is
$$
x(t)=\frac{q}{p}+\left(x_{a}-\frac{q}{p}\right) \mathrm{e}^{-p(t-a)} .
$$

5CCM211A COURSE NOTES :
$$
\frac{1}{I} \mathrm{~d} I=p(t) \mathrm{d} t
$$
and then by integration we get
$$
\ln |I(t)|=\int p(t) \mathrm{d} t .
$$
Finally we exponentiate both sides and choose $I(t)$ to be positive to give
$$
I(t)=\exp \left(\int p(t) \mathrm{d} t\right) .
$$
Given this integrating factor we should now be able to solve our general linear equation
$$
\frac{\mathrm{d} x}{\mathrm{~d} t}+p(t) x=q(t)
$$