这是一份andrews圣安德鲁斯大学 MT3503作业代写的成功案例
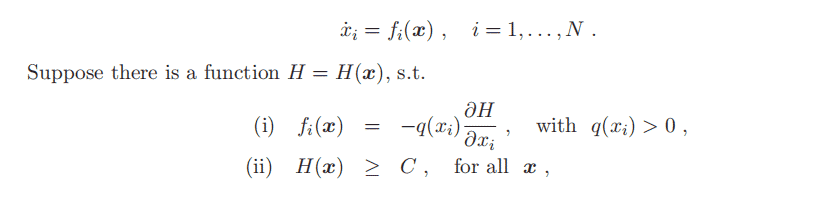
we see that $\Delta_{i}$ is asymptotically independent of $i$ in the large $c$ limit, turning into a self-consistency equation for $\Delta$, viz.
$$
\Delta=\frac{1}{i \lambda_{\varepsilon}+J^{2} \Delta}
$$
This is a quadratic equation for $\Delta$, which is solved by
$$
\Delta_{1,2}=-\mathrm{i} \frac{\lambda_{\varepsilon}}{2 J^{2}} \pm \frac{1}{2 J^{2}} \sqrt{4 J^{2}-\lambda_{\varepsilon}^{2}}
$$
Taking the limit $\varepsilon \rightarrow 0$ we have
$$
\operatorname{Re} \Delta_{i}=\operatorname{Re} \Delta= \begin{cases}\frac{1}{2 J^{2}} \sqrt{4 J^{2}-\lambda^{2}} & ;|\lambda| \leq 2 J \ 0 & ;|\lambda|>2 J\end{cases}
$$
which when inserted into finally gives
$$
\rho(\lambda)=\frac{1}{2 \pi J^{2}} \sqrt{4 J^{2}-\lambda^{2}}, \quad|\lambda| \leq 2 J
$$

MT3503 COURSE NOTES :
To show that the Gaussian integral
$$
I=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \mathrm{d} x \mathrm{e}^{-x^{2}} .
$$
is given by $I=\sqrt{\pi}$, compute
$$
I^{2}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \mathrm{d} x \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \mathrm{d} y \mathrm{e}^{-x^{2}-y^{2}} .
$$
Introducing polar coordinates $x=r \cos (\varphi), y=r \sin (\varphi)$, one has
$$
\begin{aligned}
I^{2} &=\int_{0}^{2 \pi} \mathrm{d} \varphi \int_{0}^{\infty} \mathrm{d} r r \mathrm{e}^{-r^{2}} . \
&=\frac{1}{2} \int_{0}^{2 \pi} \mathrm{d} \varphi=\pi,
\end{aligned}
$$