这是一份kcl伦敦大学学院 5CCM212A作业代写的成功案
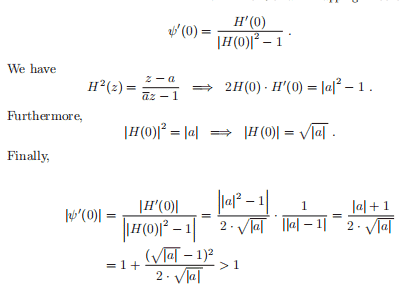

Let $S=S^{(n)}$ be a positive, even, unimodular matrix. Then $n \equiv 0 \bmod 8$.
Hint. Use the relation
$$
w:=1-\frac{1}{z}=\left(\frac{1}{1-z}-1\right)^{-1}
$$
and transform $\vartheta(S ; w)$ corresponding to these relations, by applying the formulas
$$
\vartheta(S ; z+1)=\vartheta(S ; z), \quad \vartheta(S ;-1 / z)=\sqrt{\frac{z}{i}}^{n} \vartheta(S ; z)
$$
This gives the formula
$$
\sqrt{z / i}^{n}=\sqrt{z /(i(1-z))}^{n} \sqrt{(z-1) / i}^{n} .
$$
Now specialize $z=\mathrm{i}$ in it to infer
$$
1=e^{2 \pi \operatorname{in} / 8} \text {, i.e. } n \equiv 0 \quad \bmod 8
$$

55CCM212A COURSE NOTES :
The derivative of $s \mapsto 1-p^{-s}$ is $(\log p) p^{-s}$, the logarithmic derivative being thus
$$
\frac{(\log p) p^{-s}}{1-p^{-s}}=(\log p) \sum_{\nu=1}^{\infty} p^{-\nu s}
$$
This implies
$$
-\frac{\zeta^{\prime}(s)}{\zeta(s)}=\sum_{p}(\log p) \sum_{v=1}^{\infty} p^{-\nu s}
$$